The Deauville scale and Lugano criteria
October 21, 2019The Role of Nuclear Medicine and PET CT in Neurology
What is Brain SPECT?
Brain SPECT is a nuclear medicine imaging technique rendering 3D image of brain by acquiring a 360 degree acquisition utilizing a gamma-camera. SPECT improves spatial resolution which enables the visualization of both the cortical and sub-cortical regions of the brain.
What is PET CT?
PET CT is a hybrid camera comprising of two components; the first is the PET component which is acquired when the injected radiopharmaceutical undergoes annihilation reaction and releases two positron rays at 180 degrees to each other which is then detected by the ring of detectors in the PET-scanner. The second component is a CT scan of the region being scan which enables visualization of the anatomy.
In Neurology:
The following Brain Imaging studies are currently available in South Africa:
Brain SPECT with Tc-99m- HMPAO– This scintigraphic study enables one to visualize brain perfusion. Please note that is no normal data base for brain perfusion. However, certain patterns of uptake correlates with neurological pathology.
This study is often used to evaluate the following conditions:
- Dementias, typically Fronto-temporal (Figure 1) and Alzheimer’s (Figure 2).
- In distinguishing a vasculitis from a dementia and monitoring treatment (pre and post pulsing with steroids) (Figure 3)
- Detection of Epileptic focus
- Evaluation of Cerbrovascular disease
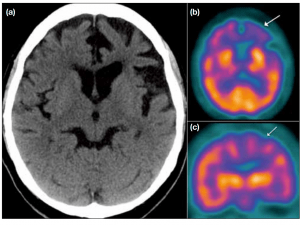
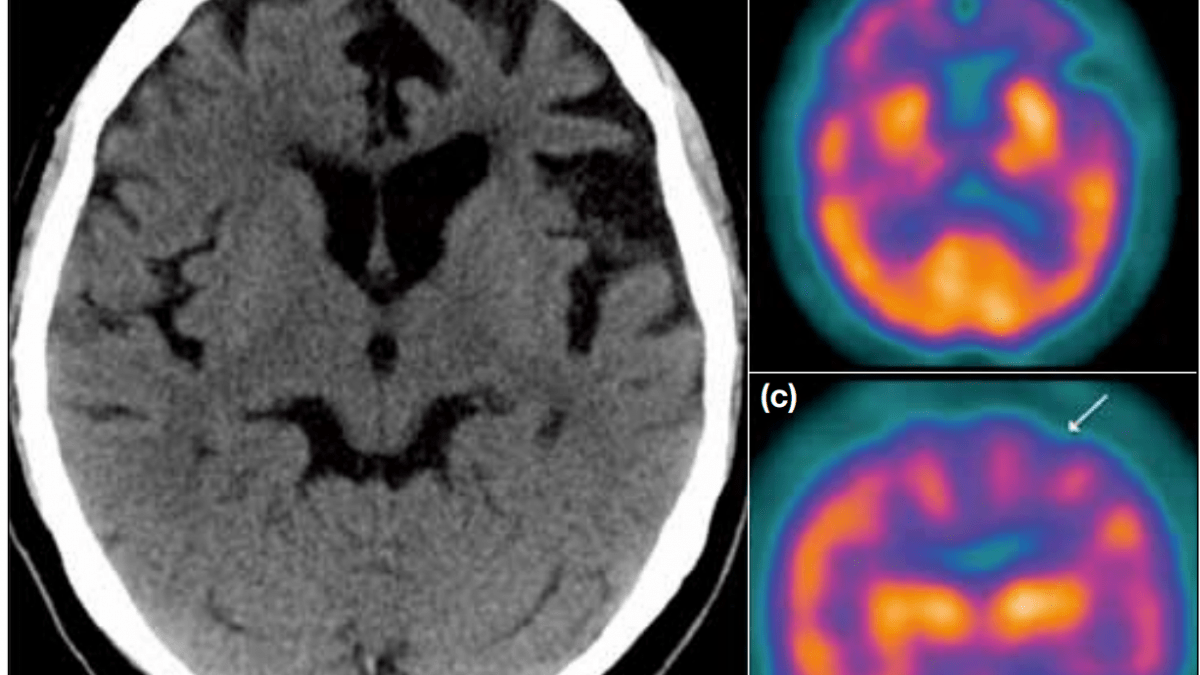
Figure 1. Axial computed tomography of the brain shows asymmetrical left frontotemporal atrophy in a patient with fronto-temporal-dementia. (b and c) Corresponding axial and
coronal Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT shows conspicuous hypoperfusion in the bilateral frontotemporal
regions, which is more severe on the left side (arrows)
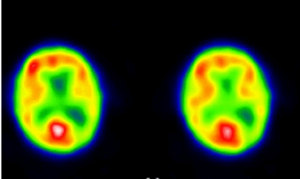
Figure 2. Note the decreased hypoperfusion to the parietal (-parietal-occipital) parts of both hemispheres
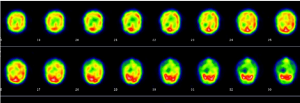 Figure 3.Tranaxial slices demonstrating poor patchy cortical uptake consistent with a vasculitis.
Figure 3.Tranaxial slices demonstrating poor patchy cortical uptake consistent with a vasculitis.
DAT Scan (I-123 ß-CIT)- This scintigraphic study is used to help distinguishing Parkinson’s from Parkinson syndrome. The radiopharmaceutical injected is I-123 Ioflupane, which has an affinity for dopaminergic neurons mostly found in the the striatum. loss of these neurons will result in decreased uptake which is most likely consistent with Parkinson’s. Figure 4.
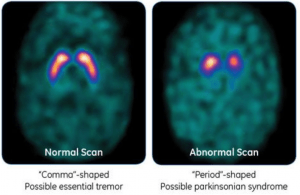 Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Metabolic Brain Imaging with F18 FDG PET CT– This study measures the metabolic activity in the brain with use of F18-FDG. Common clinical indications include:
- Dementias (Figure 5)
- Pre-surgical localization of epileptic focus
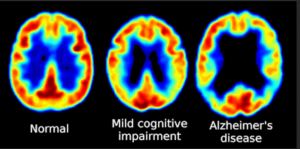
Figure 5. Note the symmetrical decreased metabolic uptake in Parietal and Occipital lobes in AD.
Neuro-receptor and Plaque Imaging in PET CT- Tau imaging with PET CT has several potential applications. PET CT imaging studies can confirm the various stages of tau deposition, and assist in the early and differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and non-Alzheimer’s disease tauopathies. Figure 6.
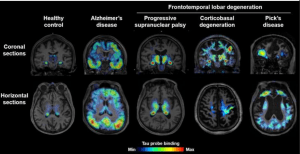
Figure 6. Tau Imaging across the Neurological Spectrum
F-18- DOPA PET CT- Used to distinguish between Parkinson’s and Parkinson like syndrome. Figure 7.
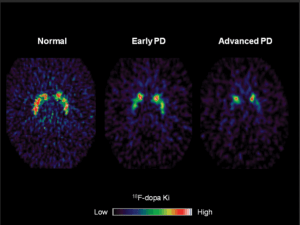
Figure 7.